![]()
NOTES ON ISSUE 10: GLOSSARY
"after his beloved
father died, when he was eight years old, his mother, too, could pinch a bit,
as it was her duty and her pleasure and her pride to do it, to help him out
in life, and put him 'prentice."
In other words, as a young boy Bounderby was sent to work as an apprentice,
a common means of training less-well-off children to a useful trade. (Recall
that early in the novel, Bounderby and Gradgrind asked why Sissy Jupe had not
been apprenticed.) Apprenticeships were also common in some of the professions;
lawyers and doctors, for instance, underwent apprenticeships for their training.
Parents wishing to apprentice their children had to find a master for them and
sign a contract stating that the child was "articled" (bound) to the
master, who received a fee. The child then usually lived and worked with the
master for a period of at least seven years. It is not clear here what trade
Bounderby was learning.
"though his mother kept but a little village
shop, he never forgot her, but pensioned me on thirty pound a year—more than
I want, for I put by out of it"
Compare this small pension—barely more than half a pound a week—to Mrs. Sparsit's
salary of £100 per year. To live on this sum and put some money aside, Mrs.
Pegler must be extremely frugal or else must still earn some small income from
her shop.
As Coketown cast ashes not only on its own head
but on the neighbourhood's too—after the manner of those pious persons who do
penance for their own sins by putting other people into sackcloth
The image of the ashes here is taken from the Catholic custom (also practiced
among High Church members of the Church of England) of sprinkling ashes on the
heads of those who have confessed on Ash Wednesday, at the beginning of Lent.
The aside concerning putting other people into sackcloth is most likely a sly
jab at strict Sabbatarians, who sought to put a stop to all amusements on Sundays
as well as to railroad travel on Sunday.
It was customary for those who now and then thirsted
for a draught of pure air, which is not absolutely the most wicked among the
vanities of life, to get a few miles away by the railroad, and then begin their
walk
Weekend "excursion trains," which were quite inexpensive, were very
popular in the industrial areas so that workers could get to the countryside
on their one day off per week, Sunday. Manchester and other industrial towns,
though highly urbanized at this period, were nevertheless surrounded by pretty
and much cleaner countryside. This railway map of South Yorkshire and Lancashire
shows the extent of the open country surrounding the great cities, as well as
the railroad connections and spur lines in the area.
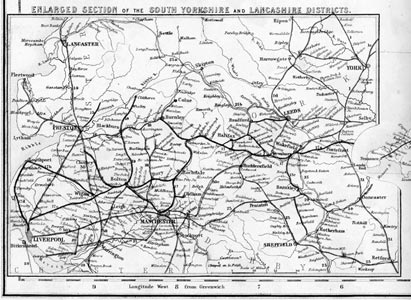
Click
on image for larger view
Mounds where the grass was rank and high, and
where brambles, dock-weed, and such-like vegetation, were confusedly heaped
together, they always avoided, for dismal stories were told in that country
of the old pits hidden beneath such indications.
The industrial areas in the north of England, as well
as the midlands, had been heavily used as mining areas and were dotted with
old, disused mines, many of them unmarked or poorly indicated. As Rachael and
Sissy know—and as we see all too clearly in the course of the chapter—these
deep, disused mine shafts could be extremely dangerous. On April 15, 1843, the
Illustrated London News published this illustration of a mine shaft that
was still in use. Note how the light just barely filters down, indicating that
the vertical shaft is quite deep.

a candle was sent down to try the air
One of the many dangers of mining was that poisonous
gases could collect in underground shafts. Sending a candle down the shaft tested
for the presence of oxygen. If the candle stayed lit, then breathable air was
present. However, since some of these gases were combustible (as in the later
reference to "fire-damp," safety lamps were used for lighting in the
mines.
"I ha' fell into th' pit, my dear, as have
cost, wi'in the knowledge o' old fo'k now livin', hundreds and hundreds o' men's
lives…. I ha' fell into a pit that ha' been wi' the' fire-damp crueler than
battle. I ha' read on ‘t in the public petition, as onnyone may read, fro' the
men that works in pits, in which they ha' pray'n and pray'n the lawmakers for
Christ's sake not to let their work be murder to ‘em…"
Fire-damp, a combustible gas, caused deadly explosions
in coal mines. Stephen here refers to the movement in the 1840s, which Dickens
had strongly and publicly supported, to improve safety measures in coal mines.
Dickens also referred to mining safety in several Household Words articles.
Rescued by a savage old postillion who happened
to be up early, kicking a horse in a fly
A postillion is a guide for a coach or other hired conveyance; a fly was a one-horse
carriage, available for hire.
A Grand Morning Performance by the Riders,
commencing at that very hour
A "morning performance" did not necessarily mean that it took place
before noon; at the time, "morning" often was used informally to mean
the part of the day before dinner, and thus a morning performance took place
in the afternoon. The word now used for such a performance is matinee, derived
from the French word matin (morning).
The Emperor of Japan, on a steady old white
horse stenciled with black spots
At the time that Hard Times was written, Japan was entirely closed to
foreigners. The Emperor of Japan was thus a suitably exotic and unknown personage
for the subject of a circus act. Several such performances at the time made
reference to Japan and the Japanese. Later in the century, as Japan opened somewhat
and the British became more interested in trade with the country, a craze for
Japanese art and design would take place, but in the 1850s this was still years
away.
if you don't hear of that boy at Athley'th,
you'll hear of him at Parith.
Astley's Royal Amphitheatre was the best-known circus of the day in England,
having been established in 1768. Although it changed venues and names several
times, it was extremely influential in changing the modes of performance in
the English circus, incorporating entertainment of all sort, from clowns to
equestrian acts. There were several well-known circuses in Paris, among them
the Cirque d'Été and the Cirque d'Hiver.
Our Children in the Wood, with their father
and mother both a-dyin' on a horthe—their uncle a-retheiving of ‘em ath hith
wardth, upon a horthe—themthelvth both a-goin' a-blackberryin' on a horth—and
the Robinth a-coming in to cover 'em with leavth, upon a horthe
This horseback act is a faithful rendition of the plot of a traditional English
ballad, the story of the Babes in the Wood, which was the basis for pantomime
and circus acts throughout the nineteenth century.
"Thath'th Jack the Giant-Killer—piethe of comic infant bithnith"
"Jack the Giant-Killer" was a popular fairy tale and thus the basis
for an act in Sleary's Circus.
"Your brother ith one o' them black thervanth."
Performances in blackface, considered comic at the time, were fairly common
in nineteenth-century circuses and other entertainments.
"There'll be beer to feth. I've never
met with nothing but beer ath'll ever clean a comic blackamoor."
Beer was indeed used to clean the faces of those who worked in blackface. Originally
burnt cork was used for blackening the face, but by the mid-nineteenth century
boot-blacking was frequently used. The derogatory term "blackamoor"
dates from the sixteenth century and derives from the use of the term Moor for
a black person.
Had he any prescience of the day, five years
to come, when Josiah Bounderby of Coketown was to die of a fit in the Coketown
street, and this same precious will was to begin its long career of quibble,
plunder, false pretences, vile example, little service and much law?
Lawsuits and disagreements over wills were often extremely protracted in the
nineteenth century, owing to the intricacies of the Court of Chancery, which
handled estate law. Dickens had made this problem the major theme of his previous
novel, Bleak House. At the time he wrote, however, Chancery was undergoing
a series of reforms that simplified court procedure in an attempt to address
the problem.